SONABLATE HIFU
High-Intensity Focussed Ultrasound (HIFU)
for targeted Therapy of Prostate Carcinoma



Earlier, precise diagnostic of prostate cancer demands a paradigm change respectively a new treatment pathway.
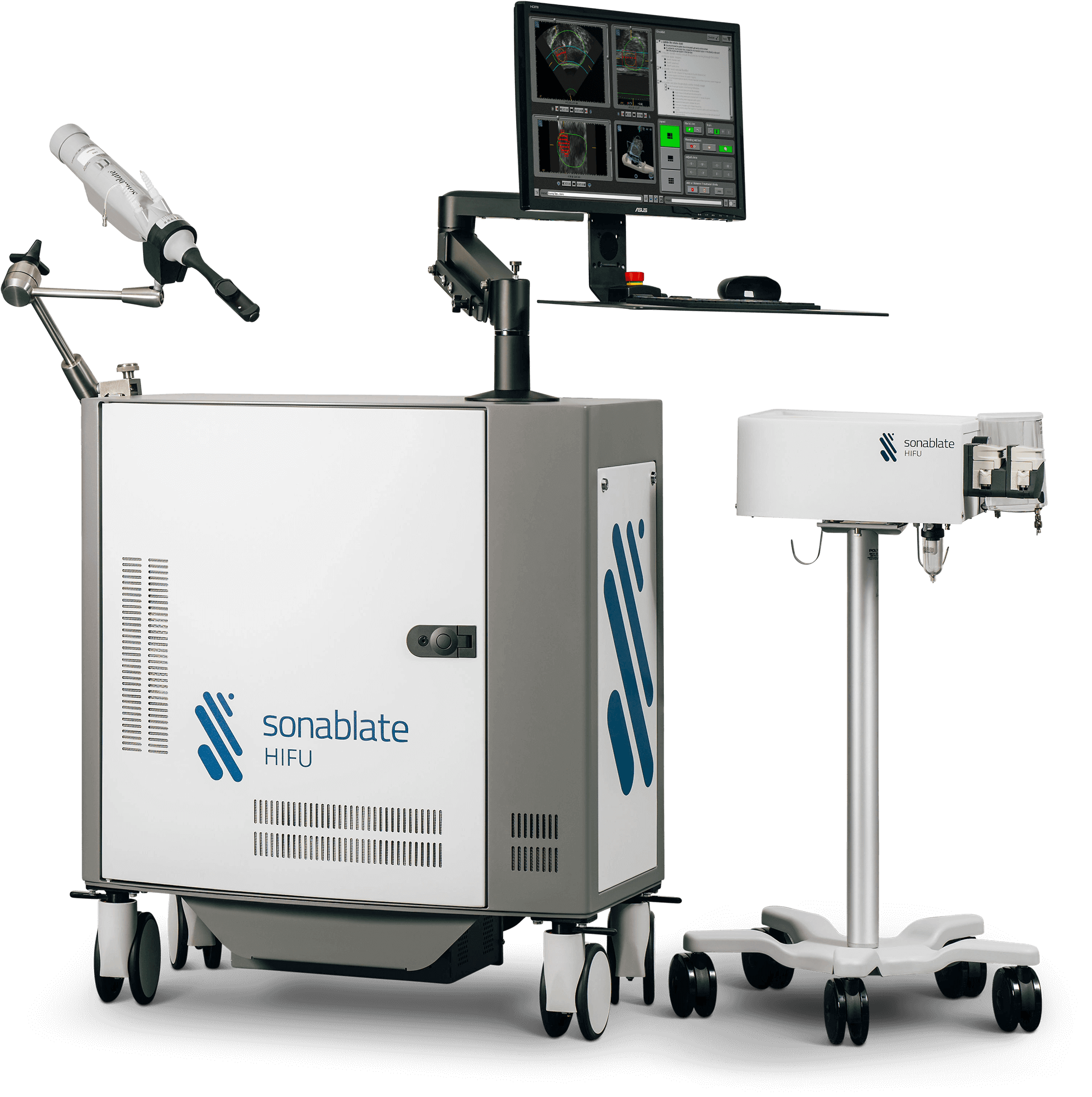
SONABLATE HIFU is the image-guided, non-invasive surgical ablation system that delivers precise, focused and controlled ablative energy and allows to create a customized treatment for each patient’s individual prostate needs.
High-intensity focused ultrasound energy is transmitted through the rectal wall and focused at desired locations within the prostate, identified by MRI and confirmed by fusion with real-time ultrasound. At the focal point of these sound waves, tissue temperature rapidly rises to almost 90 degrees Celsius, destroying the targeted tissue while surrounding tissue remains unharmed.
SONABLATE features integrated imaging and ablation transducers that are allowing to AIM, ABLATE, and ANALYZE the results of the treatment:





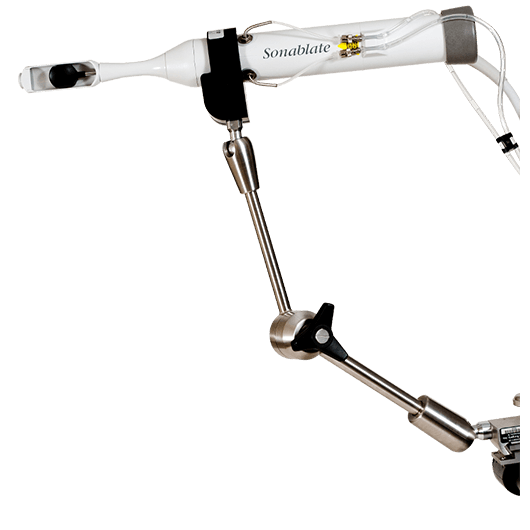

The Sonablate probe delivers precise and focused ablative energy into the prostate. Various planning and control functions allow an individually adapted treatment of the prostate.

The Sonasource console powers the Sonablate probe. It is comprised of several integrated programmable hardware and software modules that are used to drive and control SonaCare Medical's probes.
Also included with Sonasource is Sonachill, a water degasser, cooler and circulator used to ensure temperature stabilization and acoustic coupling.

It is comprised of a sterile probe tip pack and a water path kit. The probe tip allows sterile patient contact required for acoustic coupling between the target tissue and energy source.

The HIFU fusion platform follows an open architecture approach for the validated integration of existing mpMRI fusion biopsy platforms into the Sonablate planning software.
Segmented and annotated MRI images are imported into Sonablate and merged with live ultrasound images.

Features such as Tissue Change Monitoring (TCM), Total Acoustic Power (TAP), Reflexivity Index Monitor (RIM) and others enable the surgeon to respond individually to the patient's prostate and form the basis for successful, sustainable results with fewer side effects.
